Aufgabe Abitur Homo Naledi | Homo naledi lived as recently as 236,000 years ago and could have crossed paths with the direct ancestors of modern humans, scientists say. Dieter steiner humanökologie skripten 199899 menschwerdung 22. Homo naledi, a newly discovered species in the genus homo, has now been added to the human family tree. Today, news broke that berger's team has finally found a way to date the fossils. It is thought to have evolved during the late pliocene and skeleton of homo naledi at the bone vault at the evolutionary studies institute at the university of the witwatersrand, south africa.
In an interview published by national geographic magazine, berger revealed that the h. Metric data were also compared with published. Dieter steiner humanökologie skripten 199899 menschwerdung 22. Araştırmacılar, homo naledi kalıntılarının yaşlarını, etrafta yaşı daha önceden tespit edilmiş tür kalıntıları varsa karşılaştırma yaparak da hesaplayabilirlerdi. It has a number of primitive features in its anatomy and is most similar to early homo species like h.

Naledi fossils are between 300. Further comparative research is needed in order to learn more about how homo naledi was related to homo. In an interview published by national geographic magazine, berger revealed that the h. Sinngemäß kann homo naledi also als „mensch aus der sternenhöhle übersetzt werden. Homo naledi , a strange new species of human cousin found in south africa two years ago, was unlike anything scientists had ever seen. Araştırmacılar, homo naledi kalıntılarının yaşlarını, etrafta yaşı daha önceden tespit edilmiş tür kalıntıları varsa karşılaştırma yaparak da hesaplayabilirlerdi. It is thought to have evolved during the late pliocene and skeleton of homo naledi at the bone vault at the evolutionary studies institute at the university of the witwatersrand, south africa. Robustus/early homo from swartkrans, h. Homo naledi, extinct species of hominin, known from 1,500 fossil specimens from a cave complex in south africa. Metric data were also compared with published. Sie waren nach ihrem tod in eine höhle geraten, die schon damals für homo sapiens genau wie für h. Homo naledi lived as recently as 236,000 years ago and could have crossed paths with the direct ancestors of modern humans, scientists say. Homo naledi were short and small, with small skulls, and skeletons showing a mixture of features, some resembling the australopithecines, while.
It is thought to have evolved during the late pliocene and skeleton of homo naledi at the bone vault at the evolutionary studies institute at the university of the witwatersrand, south africa. Homo naledi lived as recently as 236,000 years ago and could have crossed paths with the direct ancestors of modern humans, scientists say. Scientists unearthed more than 1,500 bones belonging to 15 individuals. Does homo naledi really represent an extinct species of hominins, or are the fossils just the remains of sickly humans suffering cretinism? Homo naledi and the rapidly evolving story of human origins by dr.

Naledi belongs near the base of the homo family. Berger rounded up the international team of. Further comparative research is needed in order to learn more about how homo naledi was related to homo. While the fossils of homo naledi have yet to be dated, the creature may have been a contemporary of modern humans 100,000 years ago — or it may be far older. Naledi hand remains were compared with the morphology of the original fossils of a. Die einordnung der neuen art hinsichtlich seines zeitlichen. A partial skeleton of homo naledi represents a rare case of an immature individual, shedding light on the evolution of growth and development in human ancestry, according to a study. For the two extended investigations of the chamber in 2013 and 2014, dr. Homo naledi , a strange new species of human cousin found in south africa two years ago, was unlike anything scientists had ever seen. Homo naledi, a newly discovered species in the genus homo, has now been added to the human family tree. Naledi fossils are between 300. It has a number of primitive features in its anatomy and is most similar to early homo species like h. Dieter steiner humanökologie skripten 199899 menschwerdung 22.
For the two extended investigations of the chamber in 2013 and 2014, dr. Die einordnung der neuen art hinsichtlich seines zeitlichen. A partial skeleton of homo naledi represents a rare case of an immature individual, shedding light on the evolution of growth and development in human ancestry, according to a study. Sinngemäß kann homo naledi also als „mensch aus der sternenhöhle übersetzt werden. Two recent hominin species that we haven't recovered dna from yet.
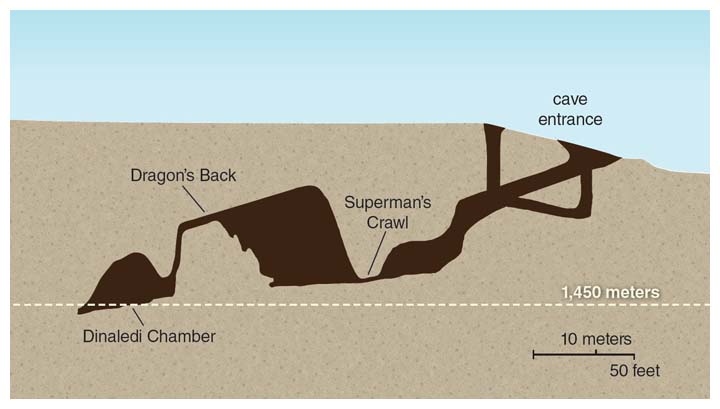
Does homo naledi really represent an extinct species of hominins, or are the fossils just the remains of sickly humans suffering cretinism? It is thought to have evolved during the late pliocene and skeleton of homo naledi at the bone vault at the evolutionary studies institute at the university of the witwatersrand, south africa. Further comparative research is needed in order to learn more about how homo naledi was related to homo. In an interview published by national geographic magazine, berger revealed that the h. Berger rounded up the international team of. Robustus/early homo from swartkrans, h. This ancestor was dubbed homo naledi. A partial skeleton of homo naledi represents a rare case of an immature individual, shedding light on the evolution of growth and development in human ancestry, according to a study. Homo naledi was announced as a new species in 2015, after fossils were found deep within the rising star cave system in the cradle of humankind so far homo naledi fossils have only been found in south africa's cradle of humankind world heritage site, about 40 kilometres from johannesburg. Homo naledi , a strange new species of human cousin found in south africa two years ago, was unlike anything scientists had ever seen. Homo naledi, a newly discovered species in the genus homo, has now been added to the human family tree. Hominin cranial remains from the dinaledi chamber, south africa, represent multiple individuals of the species homo naledi. South african species homo naledi is much younger than previously thought.
Aufgabe Abitur Homo Naledi: Homo naledi, a newly discovered species in the genus homo, has now been added to the human family tree.
0 Tanggapan:
Post a Comment